With rising concerns about climate change and an increasing demand for corporate responsibility, calculating and reducing a company’s carbon footprint has become a crucial first step in managing environmental responsibility. But what is a carbon footprint, and why should businesses quantify their emissions but actively work to reduce them?
What Is a Carbon Footprint?
A carbon footprint is the measure of total greenhouse gases (GHGs, primarily carbon dioxide (CO2), emitted into the atmosphere by an individual, organisation or product.
For businesses, this encompasses emissions from energy consumption, transportation, production processes, waste management, and even the use of third-party services. By calculating their carbon footprint, companies can understand their exact contribution to global warming and air pollution, which informs targeted actions for sustainability.
Why Is Calculating the Carbon Footprint Important?
Environmental responsibilities: By quantifying their emissions, businesses can better understand their environmental impact, and take accountability for it. Carbon footprint calculations also help to create awareness of the specific ways in which a business contributes to climate change and pollution.
Costs and savings: Typically, reducing a company's carbon footprint results in reduced operational costs. By identifying and improving areas of high energy consumption and waste, businesses will lower their overhead expenses, as well as their utility bills.
Regulatory Compliance: Governments across the world are imposing stricter regulations on emissions and carbon reporting. In the UK, large companies are required to report emissions under the Streamlined Energy and Carbon Reporting (SECR) guidelines.
Competitive Advantage: Consumers and investors are prioritising environmentally responsible companies. Having a clear carbon footprint report and a strategy for reducing emissions can enhance a company’s brand image, attract eco-conscious consumers, and appeal to investors interested in sustainable enterprises.
Risk Management: Climate change poses significant risks to business continuity, from disruptions in supply chains to increased operational costs. By understanding and addressing their carbon footprint, businesses can identify vulnerabilities and work toward long-term resilience and sustainability.
To effectively manage and reduce your company's environmental impact, it's essential to first measure your current carbon emissions. Utilising a reliable tool like the Direct Business Solutions carbon footprint calculator can provide valuable insights into your energy consumption patterns. This user-friendly tool allows you to input your business's annual energy usage, automatically retrieving data from your electricity and gas meters to calculate your carbon footprint using standard emission factors. By understanding your specific emissions, you can identify key areas for improvement, implement targeted energy-saving measures, and track your progress over time. Taking this proactive step not only aids in environmental responsibility but also enhances operational efficiency and compliance with evolving regulations.
Direct vs. Indirect Carbon Emissions
Understanding the carbon footprint requires distinguishing between direct and indirect emissions:
Direct Emissions: These types of emissions are produced directly by company-owned and controlled resources like vehicles, manufacturing facilities, and heating systems. Direct emissions are often easier to identify and quantify, but they may still require substantial changes to reduce.
Indirect Emissions: Indirect emissions come from a company's consumption of goods and services. This can include emissions generated from purchased electricity, steam, heating and cooling. It can also include emissions resulting from activities not owned or controlled by the company such as employee commutes, business travel, and supply chain processes.
Environmental impact of business emissions
Each ton of CO2 emitted into the atmosphere contributes to climate change, global warming and air pollution. Corporate emissions, particularly in sectors like manufacturing, energy, and transportation, have substantial environmental impacts, from melting ice caps to increased air pollution and extreme weather events. Reducing emissions helps curb these consequences, supporting global climate goals such as those outlined in the Paris Agreement.
Strategies for Reducing Carbon Emissions
Reducing a carbon footprint requires a proactive approach and often demands changes within the organisation.
Appoint a sustainability team: Hiring a dedicated individual or team can help to ensure that carbon reduction efforts are not only well managed but aligned with the company’s goals. They can prioritise sustainability initiatives, monitor progress, and identify further opportunities for reduction.
Invest in carbon offsetting: Carbon offsetting involves supporting projects which remove or reduce CO2 in the atmosphere to balance out the company’s own emissions. Examples include investing in reforestation projects, renewable energy initiatives, and methane capture technologies.
Re-budget travel policies: Travel is often a significant source of corporate emissions, especially for companies with international business operations. Companies can reduce their travel carbon footprint by promoting virtual meetings, setting travel caps, and moving to an electrical vehicle fleet.
Reduce Waste: Waste reduction, particularly of plastics and other non-biodegradable materials, can significantly reduce emissions. Recycling, composting, and minimising single-use products all contribute to a lower carbon footprint.
Shift to Renewable Energy: Transitioning to renewable energy sources, such as solar, wind, or hydropower, can drastically reduce indirect emissions. Many companies are making the switch by installing solar panels on-site or purchasing green energy from suppliers, benefiting both the environment and their utility budgets.
How to Calculate Your Carbon Footprint
Calculating a business’s carbon footprint can be complex, especially for larger organisations with multiple locations and supply chains. However, following these general steps can help businesses get started:
Identify emission sources: Start by listing all possible sources of emissions within the company’s operations. This includes direct sources like fuel combustion and indirect sources such as electricity use and outsourced services.
Collect data: Gather data on energy consumption, fuel use, waste generation, travel records, and any other factors that contribute to emissions. Accurate data collection is essential for calculating a reliable carbon footprint.
Engage a consultant: Many tools and calculators are available to help businesses measure their carbon footprint. Carbon accounting software, such as SIMAP, Carbon Footprint Ltd, and SBTi (Science-Based Targets initiative) guidelines, can provide accurate estimates. Alternatively, companies may hire a sustainability consultant to perform a detailed assessment.
Analyse and report: After calculating the carbon footprint, create a comprehensive report that outlines emissions sources, the total carbon footprint, and reduction targets. This report can serve as a baseline for measuring future improvements and fulfilling regulatory requirements.
Set targets and track progress: Set realistic carbon reduction targets, ideally aligned with science-based goals like those set by the Paris Agreement. Regularly monitor progress, reassess strategies, and report on advancements to stakeholders and regulatory bodies.
Calculating and reducing carbon emissions is more than a responsibility; it’s an investment in a sustainable future. By understanding their carbon footprint, companies can drive meaningful environmental change, position themselves as leaders in the eco-conscious market, and lay a solid foundation for future growth. Sustainable business practices are not just about compliance; they reflect a commitment to ethical operations, resilient growth, and a legacy of environmental stewardship. Through proactive measures like appointing sustainability managers, shifting to renewables, and setting ambitious reduction goals, businesses can make strides toward a carbon-neutral future while reaping financial and reputational rewards.
Direct Business Solutions’ Insight Tool
In a business environment where sustainability and cost-efficiency go hand in hand, Direct Business Solutions' Insight tool equips companies with the resources they need to control, reduce, and optimise their energy usage. Insight provides a comprehensive view of energy consumption patterns, including annual CO2 output and detailed, hour-by-hour heatmaps, offering in-depth analysis rarely found in standard energy monitoring tools.
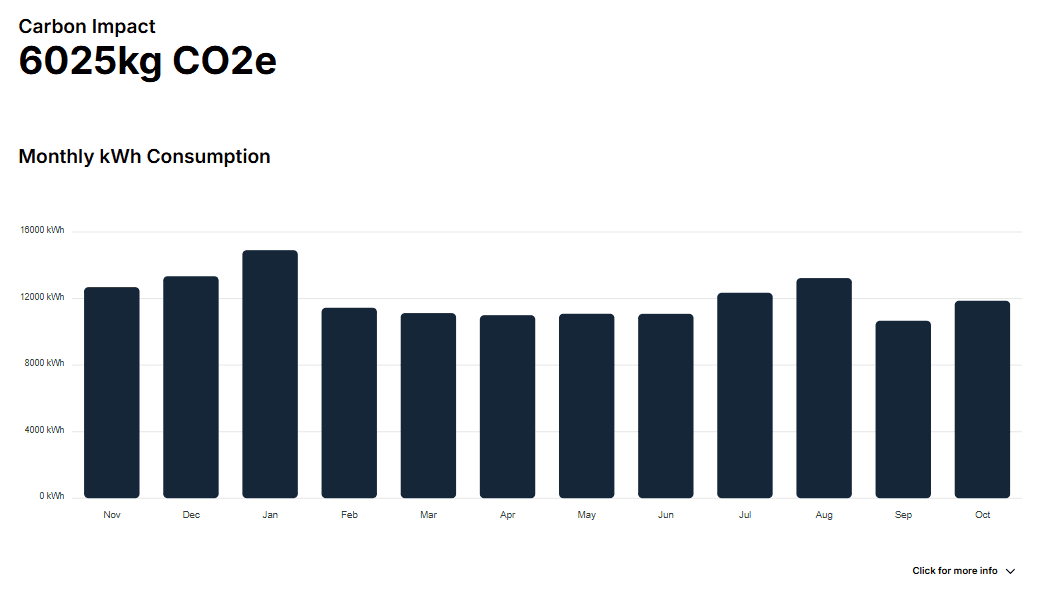
Insight doesn’t just show where energy is being used—it also highlights opportunities for improvement. By revealing the specific times, technologies, or actions contributing most to energy consumption, businesses can implement strategies to reduce their carbon footprint and achieve substantial cost savings. This could mean adjusting production schedules to avoid peak energy hours, upgrading equipment to be more energy-efficient, or enhancing facility management to limit wasted energy.
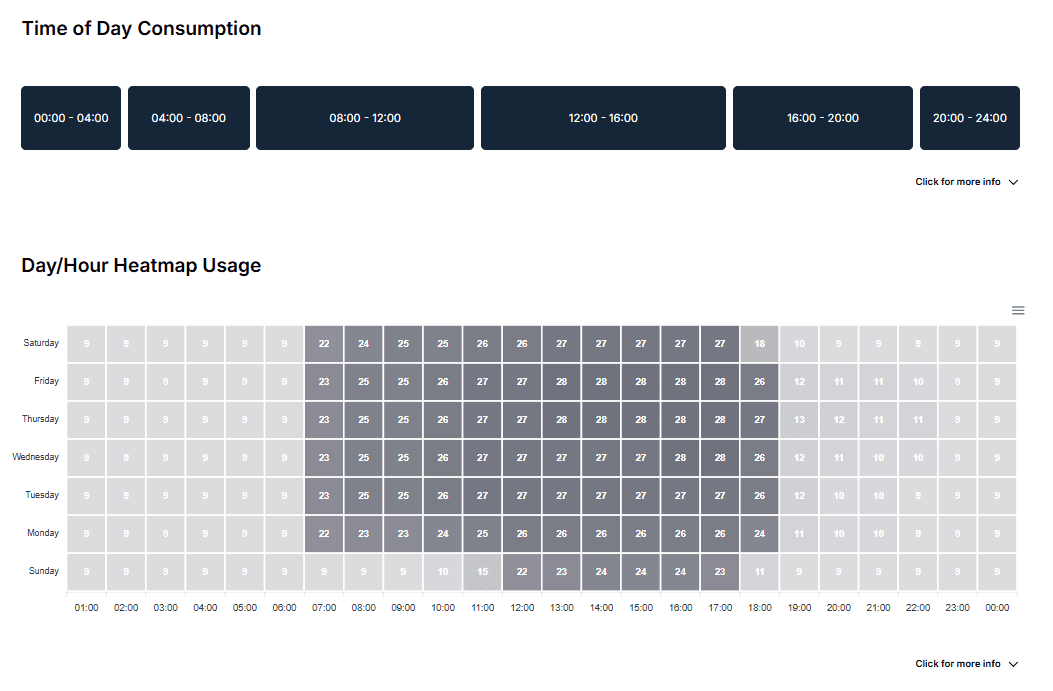
Beyond cost savings, Insight aligns with wider environmental goals and regulatory compliance needs. UK regulations, such as the Streamlined Energy and Carbon Reporting (SECR) guidelines, mandate emissions reporting, and Insight simplifies this process by providing accessible data that supports transparent, accurate reporting. The tool also helps businesses set ambitious, science-based targets for carbon reduction, ensuring that companies are not only compliant but actively contributing to climate solutions.
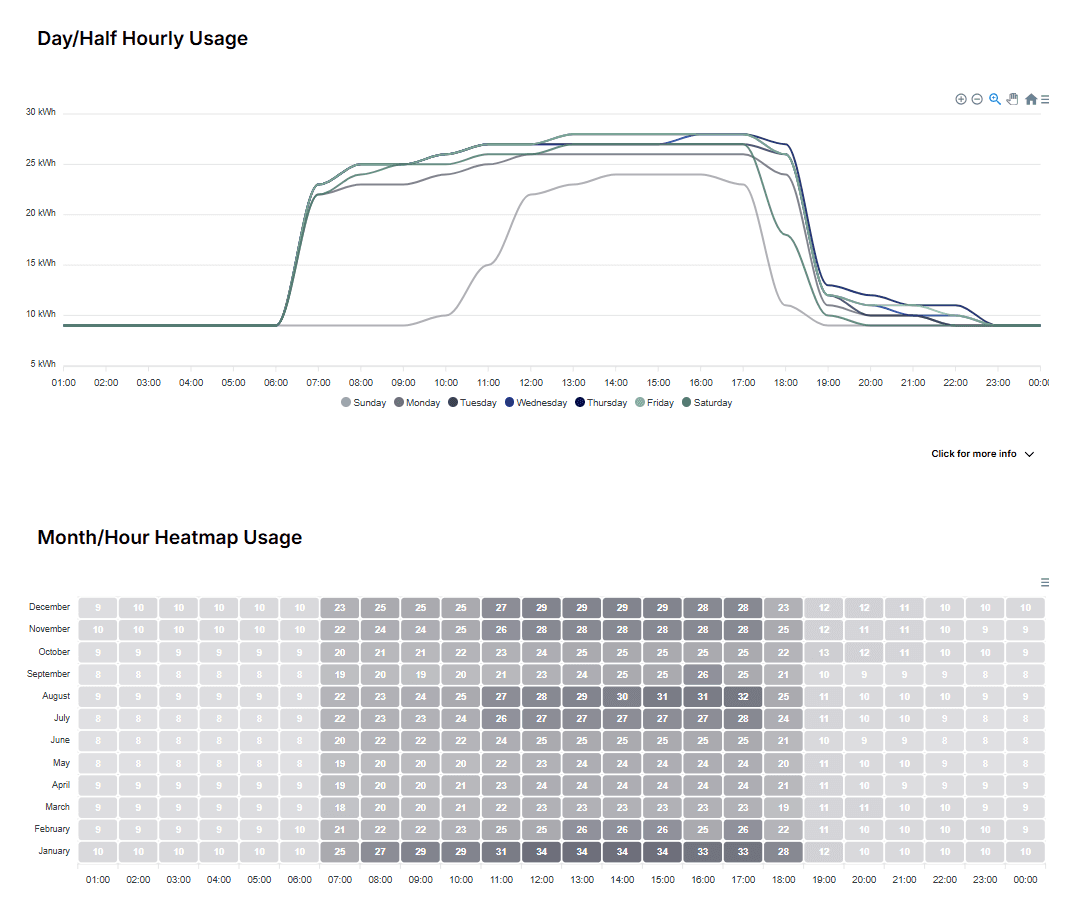
With Insight, businesses gain a powerful ally in their journey towards sustainability. Insight enhances visibility, enabling data-driven decisions that can meaningfully impact both the planet and the bottom line. By integrating Insight into their energy management strategy, companies position themselves as leaders in sustainability, driving value for stakeholders, reducing costs, and supporting the UK's transition to a low-carbon economy.